PT Energi Kaltim Persada
Written By Odezz on 12/18/2009 | 11:10 am
PT EKP lagi sering buka lowongan nih, lowongan kali ini lebih banyak ke Engineering, kesempatan buat yang lagi cari kerja atau yang pengen suasana baru..berikut iklan lowongannya dari petromindo.com update 17 Desember 2009.
 We are the one of growing fast coal company in Indonesia, there are currently operate and explore locations in the key commercial coal area East Kalimantan, South Sumatra and Papua. In response to our continuing fast growth, we need highly qualified professionals to fill the following vacancies:
We are the one of growing fast coal company in Indonesia, there are currently operate and explore locations in the key commercial coal area East Kalimantan, South Sumatra and Papua. In response to our continuing fast growth, we need highly qualified professionals to fill the following vacancies:
1. Contract Manager (CM)
Requirement:
a. Male, max age 36
b. Min bachelor degree of Law Faculty
c. Min 8 years working experiences, and 3 years in the same position
d. Familiar with contract negotiation and dealing
e. Well knowing about mine operation and mine working process
f. Familiar with mine permit
g. Full understand with budget and control in mining industry
h. Good communication and fluent in English (both written and spoken)
i. Strong leadership
j. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
2. Mine Manager (MM)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate
b. Min age 32 years old
c. Min 10 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position
d. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining
e. Have extensive technical support mining experience with surface mining operation.
f. Good Mine Plan Competencies, Budgeting and Cost Control Knowledge
g. Strong Leadership and good managerial skills
h. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
3. Senior Mine Engineer (SME)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate
b. Min age 32 years old
c. Min 10 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position
d. Have extensive technical support mining experience with surface mining operation.
e. Good Mine Plan Competencies
f. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining
g. Good organizer with managerial skills
h. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
4. Mine Engineer (ME)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring Mine Engineer
b. Min age 28 years old
c. Min 5 years working experiences and 1 years in the same position
d. Have knowledge about governmental mining regulation.
e. Familiar with computer literate Microsoft Office and MINCOM Software (SURPAC)
f. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining
i. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
5. Mine Supervisor (MS)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate
b. Min age 28 years old
c. Min 6 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position
d. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining
e. Strong Leadership and good supervisory skills
f. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
6. Mine Foreman (MF)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring Mine Engineer
b. Min age 26 years old
c. Min 3 years working experiences and 1 years in the same position
d. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining
e. Familiar with computer literate Microsoft Office and MINCOM Software (SURPAC)
f. Strong Leadership
g. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
7. Senior Mine Geologist (SMG)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate
b. Min age 32 years old
c. Min 10 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position
d. Develop & Manage Exploration Plan
e. Responsible for reliable Geological Model
f. Manage & Develop Safety System within department
g. Able to use Surpac, AutoCAD, and other Geology tools
h. Good organizer with managerial skills
i. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
8. Geologist Exploration (GE)
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring Geology
b. Min age 28 years old
c. Min 5 years working experiences in geology project and 1 years in the same position
d. referable working in Contractor Coal Mining
e. Familiar with computer literate Microsoft Office and MINCOM Software (SURPAC)
f. Strong Leadership
g. Ready to work any area in Indonesia
9. Paramedic (Prm)
Requirement:
a. Min. graduated from nursing academy
b. Min age 24 years old
c. Good knowledge of BLS (Basic Lab Support), Hyperkes & OHS.
d. Min 2 years working experiences at remote area
e. Have excellent interpersonal and communication skills
f. Eager to give the best services for your patient
g. Mature and pleasant personality with a strong personal drive
h. Ready to work any remote area in Indonesia
Your application will be treated confidentially and only short listed candidates will be followed up. Please send your detail CV & recent photograph and put the position code as your email subject to:
Paling lambat sampai 31 Desember 2009
SOP Penulisan Laporan Eksplorasi
Written By Odezz on 12/13/2009 | 5:13 pm
 Bagi semua perusahaan pertambangan, sebelum memulai usaha penambangan, tentunya harus melakukan kegiatan eksplorasi geologi atau penyelidikan lebih dahulu terhadap suatu daerah yang akan ditambang, hal ini dilakukan agar perusahaan / pemilik usaha dapat memperoleh informasi detail tentang bahan galian yang akan ditambangnya.
Bagi semua perusahaan pertambangan, sebelum memulai usaha penambangan, tentunya harus melakukan kegiatan eksplorasi geologi atau penyelidikan lebih dahulu terhadap suatu daerah yang akan ditambang, hal ini dilakukan agar perusahaan / pemilik usaha dapat memperoleh informasi detail tentang bahan galian yang akan ditambangnya.Beberapa perusahaan tambang batubara masih ada yang kurang memperhatikan penyelidikan detail terhadap kondisi bahan galian yang akan ditambang, besarnya cadangan, struktur geologi, kondisi air tanah, dan perubahan lingkungan yang diakibatkan oleh kegiatan penambangan tersebut.
Untuk menghindari hal yang tidak diinginkan tersebut diatas maka perlu dilakukan penyelidikan yang susuai dengan prosedur yang benar sesuai dengan tahapan-tahapannya. Setahu saya, umumnya tahapan ini dibagi menjadi 4 (empat) tahapan eksplorasi, yaitu :
- Survey Tinjau / Reconnaissance
- Prospeksi / Prospecting
- Survey Pendahuluan / Preliminary Exploration
- Eksplorasi Rinci / Detailed Exploration
Untuk lebih jelas mengenai tahapan eksplorasi dan standard operation procedure tentang penulisan laporan eksplorasi dapat anda lihat publikasi dari BSN - Badan Standardisasi Nasional Indonesia, dan Australian Code For Reporting of Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves (The JORC Code) dibawah ini :
1. SNI (Klasifikasi Sumberdaya & Cadangan Batubara)
Klasifikasi Sumberdaya dan Cadangan Batubara -
2. Penyusunan Berdasarkan JORC Code 2004
JORC Code 2004 -
Pedoman Klasifikasi Perhitungan Cadangan Sumberdaya Mineral & Batubara
Anda juga dapat merujuk pada klasifikasi Sumberdaya Mineral berdasarkan SNI dan JORC
Coal Mining & the Environment
Written By Odezz on 12/11/2009 | 11:12 am
Land Disturbance
In best practice, studies of the immediate environment are carried out several years before a coal mine opens in order to define the existing conditions and to identify potential problems. The studies look at the impact of mining on surface and ground water, soils, local land use, native vegetation and wildlife populations. Computer simulations can be undertaken to model impacts on the local environment. The findings are then reviewed as part of the process leading to the award of a mining permit by the relevant government authorities.Mine Subsidence
Mine subsidence can be a problem with underground coal mining, whereby the ground level lowers as a result of coal having been mined beneath. A thorough understanding of subsistence patterns in a particular region allows the effects of underground mining on the surface to be quantified.
Water Pollution
Mine operations work to improve their water management, aiming to reduce demand through efficiency, technology and the use of lower quality and recycled water. Water pollution is controlled by carefully separating the water runoff from undisturbed areas from water which contains sediments or salt from mine workings. Clean runoff can be discharged into surrounding water courses, while other water is treated and can be reused such as for dust suppression and in coal preparation plants.
Acid mine drainage
Acid mine drainage (AMD) can be a challenge at coal mining operations. AMD is metal-rich water formed from the chemical reaction between water and rocks containing sulphur-bearing minerals. The runoff formed is usually acidic and frequently comes from areas where ore- or coal mining activities have exposed rocks containing pyrite, a sulphur-bearing mineral.
However, metal-rich drainage can also occur in mineralised areas that have not been mined. AMD is formed when the pyrite reacts with air and water to form sulphuric acid and dissolved iron. This acid run-off dissolves heavy metals such as copper, lead and mercury into ground and surface water.

There are mine management methods that can minimise the problem of AMD, and effective mine design can keep water away from acid generating materials and help prevent AMD occurring. AMD can be treated actively or passively.
- Active treatment involves installing a water treatment plant, where the AMD is first dosed with lime to neutralise the acid and then passed through settling tanks to remove the sediment and particulate metals.
- Passive treatment aims to develop a self-operating system that can treat the effluent without constant human intervention.
Dust & Noise Pollution
Dust at mining operations can be caused by trucks being driven on unsealed roads, coal crushing operations, drilling operations and wind blowing over areas disturbed by mining.Dust levels can be controlled by spraying water on roads, stockpiles and conveyors. Other steps can also be taken, including fitting drills with dust collection systems and purchasing additional land surrounding the mine to act as a buffer zone. Trees planted in these buffer zones can also minimise the visual impact of mining operations on local communities.
Noise can be controlled through the careful selection of equipment and insulation and sound enclosures around machinery.
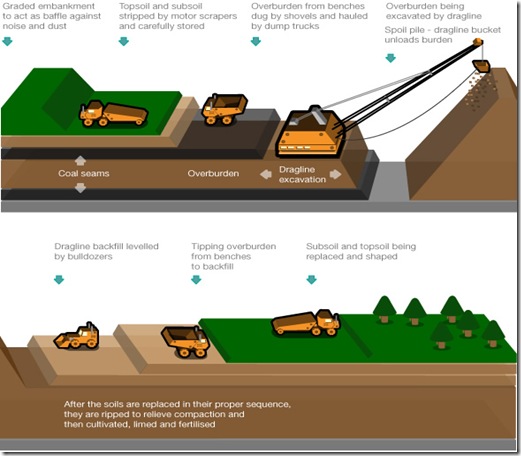
Rehabilitation
Coal mining is only a temporary use of land, so it is vital that rehabilitation of land takes place once mining operations have stopped. In best practice a detailed rehabilitation or reclamation plan is designed and approved for each coal mine, covering the period from the start of operations until well after mining has finished.Where the mining is underground, the surface area can be simultaneously used for other uses - such as forests, cattle grazing and growing crops - with little of no disruption to the existing land use.
Mine reclamation activities are undertaken gradually – with the shaping and contouring of spoil piles, replacement of topsoil, seeding with grasses and planting of trees taking place on the mined-out areas. Care is taken to relocate streams, wildlife, and other valuable resources.
As mining operations cease in one section of a surface mine, bulldozers and scrapers are used to reshape the disturbed area. Drainage within and off the site is carefully designed to make the new land surface as stable and resistant to soil erosion as the local environment allows. Based on the soil requirements, the land is suitably fertilised and revegetated. Reclaimed land can have many uses, including agriculture, forestry, wildlife habitation and recreation.
Companies carefully monitor the progress of rehabilitation and usually prohibit the use of the land until the vegetation is self-supporting. The cost of the rehabilitation of the mined land is factored into the mine’s operating costs.
Using Methane from Coal Mines
Methane (CH4) is a gas formed as part of the process of coal formation. It is released from the coal seam and the surrounding disturbed strata during mining operations. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential 23 times that of carbon dioxide. While coal is not the only source of methane emissions – agricultural activities are major emitters – methane from coal seams can be utilised rather than released to the atmosphere with a significant environmental benefit.Sumber: worldcoal.org
Coal Mining Methods
Written By Odezz on 12/09/2009 | 9:58 pm
Ada 2 metode penambangan batubara, yaitu:
- Tambang Terbuka / Open Pit Mining/ Surface Mining” dan
- Tambang Tertutup / Underground Mining
Surface Mining / Tambang Terbuka
Surface Mining - juga dikenal sebagai opencast atau opencut – metode ini akan lebih bernilai ekonomis jika lapisan batubara dekat dengan permukaan. Metode ini memiliki proporsi Recovery Batubara lebih baik atau lebih tinggi daripada tambang bawah tanah, Recovery mencapai 90% atau lebih dari batubara yang akan ditambang.
Tambang terbuka dapat mencakup wilayah yang sangat luas, dengan menggunakan perlengkapan alat berat yang bervariasi, pemilihan alat berat yang digunakan tergantung dari perhitungan ekonomis suatu deposit batubara, alat berat tersebut adalah :
- Driglines
- Power Sovel / Excavator
- Dump Truck (Mining Truck)
- Buldozer
- Bucket Wheel Excavator
- Conveyors
Underground Mining / Tambang Tertutup
Ada dua metode penambangan bawah tanah/ tambang tertutup: room-and-pillar dan longwall mining.
Room & Pillar Mining
Pada metode ini, deposit batubara yang ditambang dengan membuat jaringan ‘ruangan’ didalam lapisan batubara dan menyisakannya sebagai 'pilar' batubara untuk mendukung atap tambang. Pilar ini dapat mencapai 40% dari total batubara, kadang-kadang jika memungkinkan pillar batubara tersebut dapat di tambang pada fase berikutnya.

Longwall Mining, metode ini bertujuan memaksimalkan recovery pengambilan batubara / ekstraksi batubara, atau 'face' / permukaan dengan menggunakan alat pengupas mekanis. Metode ini dibutuhkan perencanaan yang akurat, dan harus dipastikan kondisi geologi batubaranya ada di seluruh bagian sebelum pekerjaan pembangunan dimulai. permukaan batubara yang akan dipotong bervariasi panjangnya dari 100-350m. Hydraulically-powered menyangga lapisan atap sementara terus naik ke atap dan batubara diekstrak. Ketika batubara telah diekstraksi, atap akan runtuh dalam kondisi tertentu. Lebih dari 75% dari deposit batubara yang dapat dicover dari panelbatu bara.

Kemajuan teknologi telah membuat pertambangan batubara saat ini lebih produktif dari sebelumnya. Untuk mengikuti perkembangan teknologi dan untuk mengambil batu bara seefisien mungkin harus memiliki pekerja tambang yang sangat terampil dan terlatih dalam penggunaan instrumen dan peralatan.
Sumber: Dari berbagai sumber
Lowongan di PT Energi Kaltim Persada
URGENTLY REQUIRED
We are the one of growing fast coal company in Indonesia, there are currently operate and explore locations in the key commercial coal area East Kalimantan, South Sumatra and Papua. In response to our continuing fast growth, we need highly qualified, dynamic, energetic, strong leadership and experienced professionals to fill the following vacancies:
1. CPP (Coal Preparation Plan) Supervisor – CPPS
Requirement:
a. University Graduate,
b. Male, max 38 years old,
c. Min 5 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position,
d. Having POP Certificate,
e. Well organized on coal production target in ROM stock,
f. Excellent at monitoring and reporting the production facility condition, and the plan barging,
g. Able to make a daily and monthly report of Crusher, MBL, and BLC production,
h. Strong leadership and hard working,
i. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
2. Sr. Mine Geologist – SrMG
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring in Geology,
b. Max age 38 years,
c. Min 5 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position,
d. Having POP Certificate,
e. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining,
f. Familiar with computer literate Microsoft Office and MINCOM, SURPAC,
g. Expert in all activities and coal handling from Pit to Port,
h. Strong leadership and hard working,
i. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
3. Sr. Mine Surveyor – SrMS
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring in Geology or Mine Engineering,
b. Max age 38 years,
c. Min 6 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position,
d. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining,
e. Excellent at monitoring and reporting daily, weekly, and monthly topographic survey targets,
f. Mastering to use SOKIA, AutoCAD to plot daily topographic data and to calculate coal stock in the stockpile,
g. Strong leadership and hard working,
h. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
4. Maintenance Supervisor – MTS
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring in Electrical Engineering,
b. Male, max age 38 years old,
c. Min 6 years working experiences and 2 years in the same position,
d. Preferable working in Contractor Coal Mining,
e. Having experiences on : Plant Maintenance, Instrumentation Electrician, Electrician Camp Maintenance, Crusher Plant, Conveyor, Powerhouse (Generator Set),
f. Having POP Certificate,
g. Strong Leadership and hard working,
h. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
5. Civil Supervisor – CS
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring in Civil Engineering,
b. Male, max 38 years old,
c. Min 5 years experiences, preferably working in mining industry,
d. Having experiences to coordinate subcontractors, supplier and team member for the successful completion civil project,
e. Expert in using computer engineering software,
f. Strong leadership and hard working,
g. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
6. Administration Supervisor – AdS
Requirement:
a. University Graduate, majoring in Administration or Management,
b. Male, max 38 years old,
c. Having minimum at least 6 years experiences, and 2 years in the same position,
d. Understand of Personnel System and Legal,
e. Familiar with Mining & PEB Document Permit,
f. Strong Leadership, Discipline and hard working,
g. Ready to work any area in Indonesia.
Your application will be treated confidentially and only short listed candidates will be followed up. Please send your detail CV & recent photograph and put the position code as your email subject to:
Expiry date: December 16, 2009
Kamus Istilah Pertambangan
Written By Odezz on 12/07/2009 | 5:32 pm

Open-pit mine
Type of mining that is used for shallow deposits; coal or ore is extracted by digging a succession of benches from the surface of the ground downward.Crater
Depression that forms the bottom of the quarry; it is a result of the extraction of deposits.Haulage road
Access road leading to the quarry; it is used to haul coal to the treatment plant.Ore
Solid fossil fuel that is black and contains a large amount of carbon.Bench height
Vertical distance between the horizontal planes of two benches.Ramp
Roadway between two benches; it is inclined so that motorized vehicles can remove the ore extracted from the various levels.Overburden
Part of the ground that covers the ore beds; it is removed to reach the deposit.Ground surface
The land that covers the deposit.Face
Vertical surface created by dynamiting a deposit to extract its ore.Bench
The levels of a quarry that are arranged like steps of a staircase and from which coal or ore is extracted.
Where is Coal Found?
Written By Odezz on 12/04/2009 | 9:40 pm

It has been estimated that there are over 847 billion tonnes of proven coal reserves worldwide. This means that there is enough coal to last us over 130 years at current rates of production. In contrast, proven oil and gas reserves are equivalent to around 42 and 60 years at current production levels.
Coal reserves are available in almost every country worldwide, with recoverable reserves in around 70 countries. The biggest reserves are in the USA, Russia, China and India. After centuries of mineral exploration, the location, size and characteristics of most countries' coal resources are quite well known. What tends to vary much more than the assessed level of the resource - i.e. the potentially accessible coal in the ground - is the level classified as proved recoverable reserves. Proved recoverable reserves is the tonnage of coal that has been proved by drilling etc. and is economically and technically extractable.
Definitions
ResourceOver recent years there has been a fall in the reserves to production (RP) ratio, which has prompted questions over whether we have reached 'peak coal'. Peak coal is the point in time at which the maximum global coal production rate is reached after which the rate of production will enter irreversible decline. However, recent falls in the RP ratio can be attributed to the lack of incentives to prove up reserves, rather than a lack of coal resources. Exploration activity is typically carried out by mining companies with short planning horizons rather than state-funded geological surveys. There is no economic need for companies to prove long-term reserves.
The amount of coal that may be present in a deposit or coalfield. This does not take into account the feasibility of mining the coal economically. Not all resources are recoverable using current technology.
Reserves
Reserves can be defined in terms of proved (or measured) reserves and probable (or indicated) reserves. Probable results have been estimated with a lower degree of confidence than proved reserves.
Proved Reserves
Reserves that are not only considered to be recoverable but can also be recovered economically. This means they take into account what current mining technology can achieve and the economics of recovery. Proved reserves will therefore change according to the price of coal; if the price of coal is low proved reserves will decrease.
All fossil fuels will eventually run out and it is essential that we use them as efficiently as possible. Coal reserves could be extended further through a number of developments including:
- the discovery of new reserves through ongoing and improved exploration activities;
- advances in mining techniques, which will allow previously inaccessible reserves to be reached.
Coal Exploration
Coal reserves are discovered through exploration activities. The process usually involves creating a geological map of the area, then carrying out geochemical and geophysical surveys, followed by exploration drilling. This allows an accurate picture of the area to be developed. The area will only ever become a mine if it is large enough and of sufficient quality that the coal can be economically recovered. Once this has been confirmed, mining operations begin.worldcoal.org